Understanding why CORS matter
Ensuring the security of user data is crucial. One critical mechanism that aids in this endeavor is Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS).
The Cross-Origin Request Vulnerability
Consider a user who is authenticated on example.com, a SaaS platform. If this user visits a malicious site, say malicious-website.com, that site could execute the following script:
fetch("https://api.example.com/delete-all-customers", {
method: "POST",
credentials: "include"
});
Here, the browser attaches AUTOMATOCALLY the user’s credentials (like cookies or JWTs stored on the browser) associated with api.example.com to the request. Consequently, api.example.com might process this unauthorized request, leading to potential data breaches or loss.
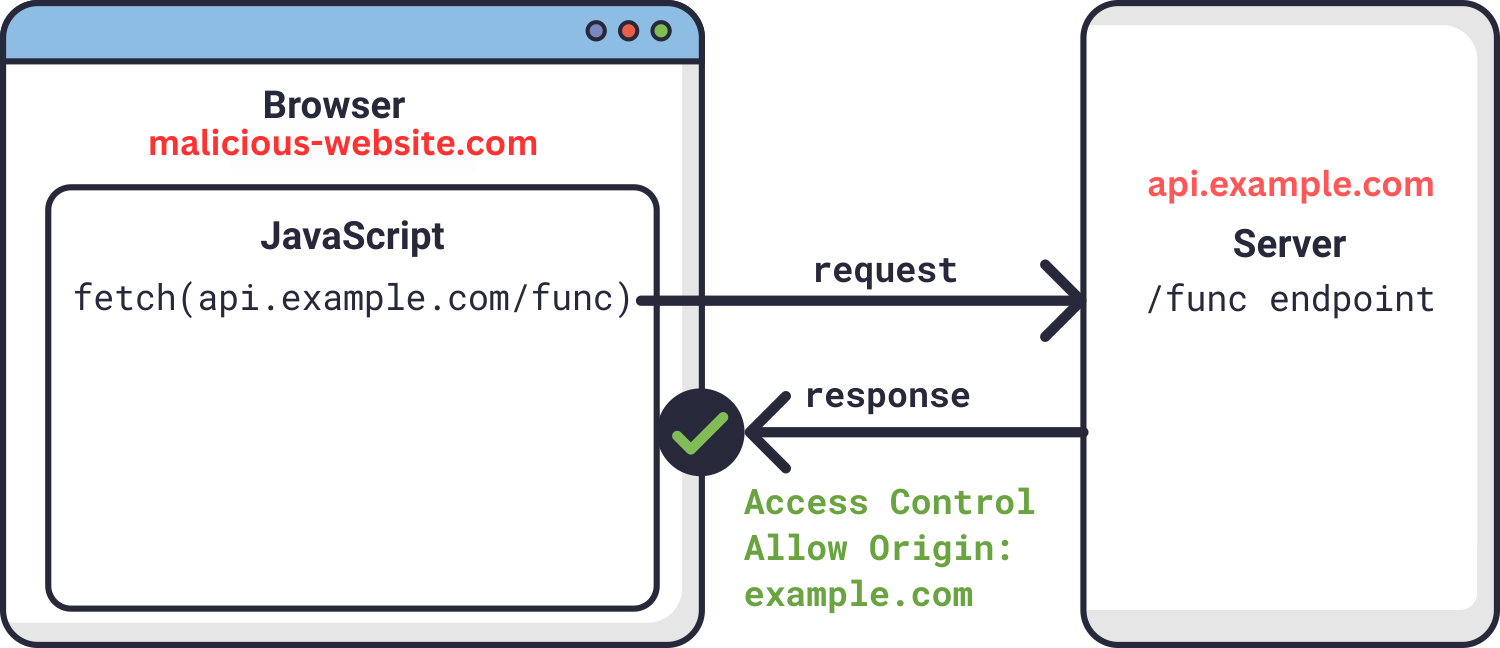
The Role of CORS in Mitigation
CORS serves as a safeguard against such vulnerabilities. By configuring the server at api.example.com to allow requests only from trusted origins, the malicious request from malicious-website.com would be blocked by the browser, preventing unauthorized actions.
Implementing Effective CORS Policies
To enhance security:
- Specify Allowed Origins: Configure the server to permit requests solely from trusted domains, such as:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: https://example.com Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true - Utilize SameSite Cookies: Set cookies with the SameSite attribute to Lax or Strict, ensuring they aren’t sent with cross-origin requests.
Conclusion
CORS acts as a defense mechanism, preventing unauthorized websites from exploiting user credentials and interacting with your application’s API.



