You want to learn how to use Jupyter, the best way to develop in python ? Here is what you can do
Tested Configuration:
MacOS: Sierra 10.12
Anaconda: 5.1
Jupyter notebook: 5.4.0
Browser: Google Chrome v64
1. Pre requisite
Install Anaconda following this link
It will set up the environment for you so you don’t have to worry about compatibilities
2. Start Jupyter
Open the Anaconda Navigator application. It will prompt a screen like this one:

Then click on the Launch button for Jupyter Notebook.
It will open a tab on your internet browser like the following:
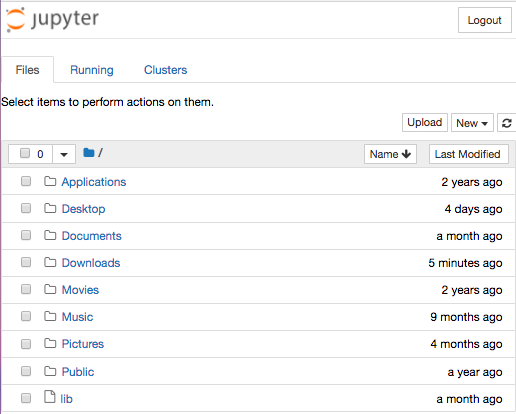
Note that there are 3 tabs: Files, Running and Clusters.
Only the Files tab allow you to open or create notebooks.
3. Create a Notebook
Super Easy: click Python 3
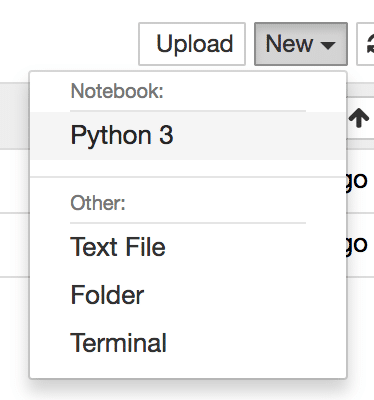
Name it (by clicking on ‘Untitled’)
By giving it a name, the notebook will be saved as a file with extension .ipynb
Now if you come back to the Files tab, you see your new file. I named it test and as you can see, its status is “running” because I left it open.
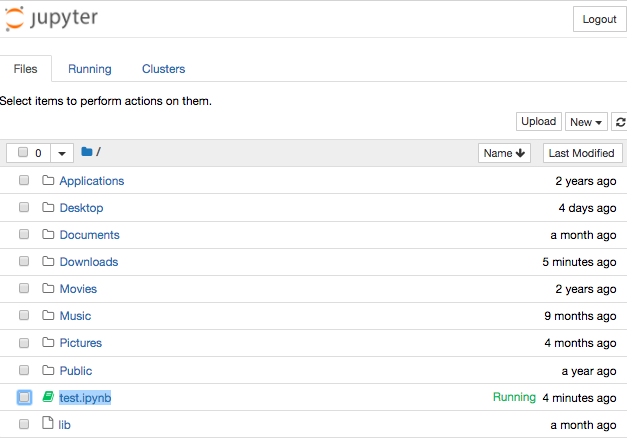
3. Edit your Notebook
Code VS Markdown: there is a cell type on the right. It lets you choose between commenting your code (using Markdown) or writing python code (selecting code).
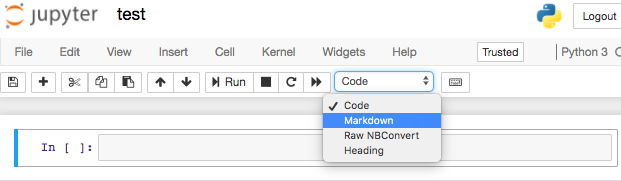
Let’s practise with commenting First line of comment on top of a python code that returns the string printed out
How to validate one cell: type <Shift> + <Enter>
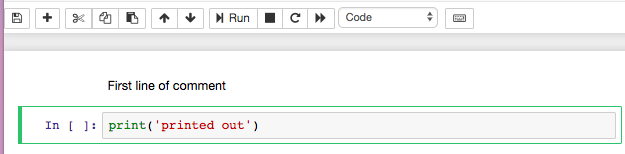
Note: type Esc to exit the edit mode of a cell
Note: All key shortcuts, simply go to Help → Keyboard Shortcuts
My favorites:
- Insert Cell: <Esc> + <b>
- Delete Cell: <Esc> + <d> + <d>
- Copy & paste Cell: Select a cell + <Esc> + <c> + <v>
- Split Cell: <Ctrl> + <Shift> + <->
4. Commit your script
If you don’t know what commit stands for: read this
A cool function of Jupyter Notebook is the ability to create checkpoint, which basically are Jupyter way for commiting your script.
- Create a new checkpoint: go to File and click on Save and Checkpoint. The notebook is saved at this current state.
- Go back to a previous checkpoint: go to File, then Revert to Checkpoint and click on the checkpoint you want.
5. Export your Notebook
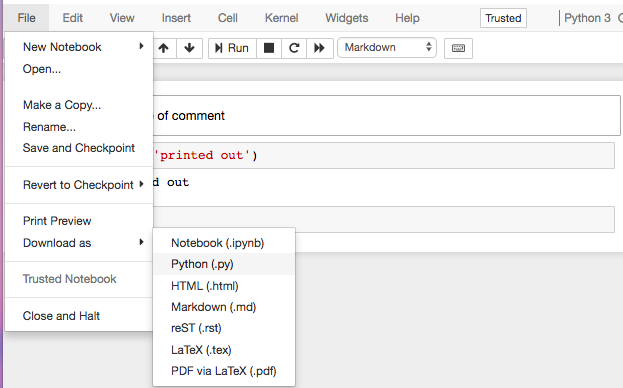
You will probably use Jupyter as an editor, and then you will need to get your python code out of Jupyter.
Easy: go to File → Download as
6. Change the Root folder
If you come back to the Files tab, you see every folder. And you can modify what you want, so some mistakes may happen… like deleting the folder “Documents” simply using the Jupyter.
That’s why we will change the default Folder / to a specific folder like this /Users/username/the/path/you/want/
-
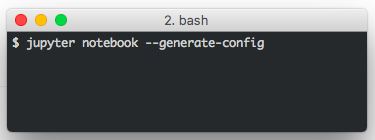
In a Terminal run:
jupyter notebook --generate-config
-
This writes a file called jupyter_notebook_config that we need to open with the command
sudo nano /Users/username/.jupyter/jupyter_notebook_config.py -
And replace the following line:
#c.NotebookApp.notebook_dir = ''
by
c.NotebookApp.notebook_dir = '/Users/username/the/path/you/want/'
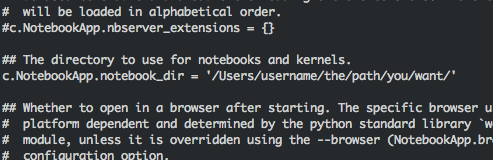
And now it looks like this:
Now your safe ! Enjoy
7. Quick notes
- If you want to use a Bash command into the notebook use
!. So for instance to change directory:!cd ..or!ls - If you want to get help from Jupyter, use
?. For instance, to get help on pprint:?pprint



